
25/08/2025

pareidolia
In modern healthcare, medical imaging is indispensable for diagnosing diseases, guiding treatments, and monitoring outcomes. However, the true value of imaging does not end with capturing scans — it extends into how these images are annotated, segmented, and prepared for AI-driven analysis.
Quality Control (QC) in medical imaging is the cornerstone of ensuring accuracy at every stage, from image capture to data labeling. Without robust QC measures, errors in segmentation or annotation can compromise AI models, misinform clinicians, and ultimately affect patient outcomes.
What is Quality Control in Medical Imaging?
Quality control in medical imaging involves a systematic approach to verifying accuracy, consistency, and reliability across both the imaging equipment and the annotated datasets derived from it. While equipment calibration remains vital, in today’s AI-powered medical landscape, QC extends deeply into:
- Annotation Verification – ensuring that labels applied to organs, tumors, or pathologies are precise and clinically valid.
- Segmentation Accuracy – validating that boundaries drawn around anatomical structures are consistent and accurate across datasets.
- Data Integrity – checking for mislabeling, missing segmentations, or inconsistencies.
- Compliance with Regulatory Standards – aligning with frameworks such as TGA (Australia), MHRA (UK), and HIPAA (USA).
Why Quality Control is Critical in Image Annotation & Segmentation
1. Accurate Diagnosis
High-quality annotations and segmentations ensure that AI-powered tools provide clinicians with reliable insights. Poor-quality labels can lead to misdiagnosis or oversight of critical conditions.
2. Patient Safety
When annotations are inaccurate, treatment plans such as radiation therapy or surgical planning may be compromised, putting patients at risk.
3. AI & Machine Learning Reliability
AI models are only as good as the data they learn from. Errors in annotation directly translate into flawed predictions, weakening trust in AI-driven healthcare.
4. Regulatory Compliance
Countries such as the UK and Australia require strict QC validation before annotated imaging datasets can be used in clinical or research contexts.
Key Components of Quality Control in Annotation & Segmentation
-
Annotation Accuracy
- Double-review processes by clinical experts.
- Consensus-based validation for complex cases.
- Double-review processes by clinical experts.
-
Segmentation Consistency
- Automated checks on segmentation masks for boundary precision.
- Cross-modality comparisons (e.g., CT vs MRI).
- Automated checks on segmentation masks for boundary precision.
-
Image Quality Assurance
- Ensuring resolution, contrast, and noise levels meet minimum thresholds before annotation begins.
-
Standardized Protocols
- Use of documented annotation guidelines to minimize variability across annotators.
The Role of AI in Quality Control
Artificial intelligence is not just the end-user of annotated data—it is also a powerful tool for quality control:
- Automated Error Detection – flagging incomplete or inconsistent labels.
- Predictive Maintenance for Datasets – identifying drift or inconsistency in annotations over time.
- Annotation Validation – AI models comparing human-drawn segmentations with algorithmic benchmarks.
Quality Control in Australia & the UK
- Australia (TGA): Requires strict QC audits of imaging datasets for AI/ML applications in diagnostics.
- UK (MHRA & CQC): Enforce safety and accuracy standards for annotated data used in clinical decision support.
These frameworks ensure that imaging datasets used in healthcare and research maintain the highest possible quality.
Future of Quality Control in Medical Imaging
The future of QC will rely heavily on automation, cloud-based annotation platforms, and AI-driven auditing tools. Features like real-time annotation feedback, automated segmentation validation, and collaborative review environments will make data preparation faster, safer, and more accurate.
Quality control is the foundation of accurate medical imaging, annotation, and segmentation. By ensuring the reliability of imaging datasets, healthcare providers and researchers can deliver more precise diagnoses, safer treatments, and more powerful AI innovations.
Whether it’s a radiologist interpreting scans, or an AI system learning from labeled data, QC ensures that every decision is built on a foundation of trust and accuracy.


01/12/2025

pareidolia
The Secret Key to Better AI Diagnosis: Why Accurate Segmentation is the best Way to Save Hypodense Lesion Prediction
In today’s medical imaging world, accuracy alone is no longer enough. Healthcare teams need to…
Read More

18/11/2025

pareidolia
The Blueprint for Better Stroke Care:How Pareidolia’s Precise Annotations Are Training Life-Saving AI
In 2025, stroke is the second leading cause of death globally, causing 3.6 million deaths.…
Read More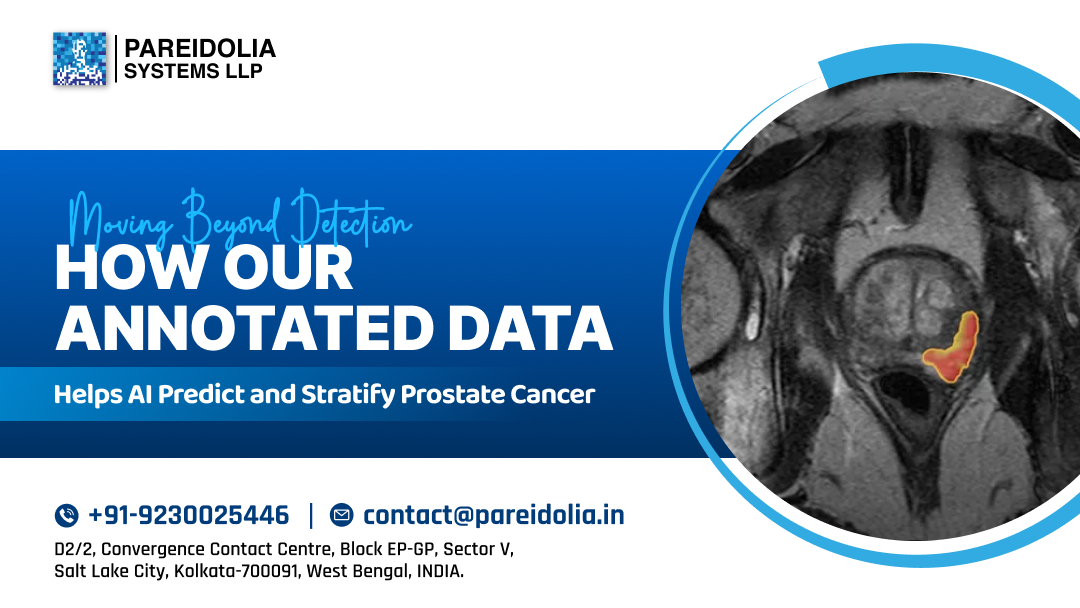

04/11/2025

pareidolia
Moving Beyond Detection: How Our Annotated Data Helps AI Predict and Stratify Prostate Cancer
Approximately 1.5 million men were diagnosed with prostate cancer globally. Prostate cancer is the fourth…
Read More
04/11/2025

pareidolia
Beyond the Pixel: How Precise ICH Segmentation Transforms Patient Care
In modern healthcare, the fusion of artificial intelligence (AI) and medical imaging is revolutionizing diagnostics…
Read More

16/10/2025

pareidolia
Accurate Segmentation with Tomosynthesis Mammography:Creating 3D Mammogram Lesion Detection AI
Breast cancer remains one of the most prevalent and life-threatening diseases affecting women globally. Early…
Read More