Apr 17 2025
medical image analysis
What is Medical Image Analysis, and How is it Done?
Medical image analysis is a critical field that merges healthcare with advanced computational techniques to extract meaningful insights from medical imaging data. From detecting diseases at early stages to guiding complex surgical procedures, it plays an essential role in diagnosis, treatment planning, and patient management. With the increasing volume of imaging data and the demand for accurate and efficient interpretation, this field has rapidly evolved, especially with the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and deep learning technologies.
Understanding Medical Imaging Modalities
Medical imaging refers to a range of techniques used to visualize the internal structures and functions of the body. Each modality serves specific clinical purposes:
- X-rays: Widely used for bone fractures, chest imaging, and dental diagnostics.
- Computed Tomography (CT): Combines multiple X-ray images to generate cross-sectional views, ideal for detecting internal injuries, tumors, and vascular diseases.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Utilizes magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of soft tissues such as the brain, spinal cord, and joints.
- Ultrasound: Employs sound waves for real-time imaging of soft tissues, commonly used in obstetrics, cardiology, and abdominal assessments.
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET): Visualizes metabolic activity and is often combined with CT or MRI for oncology and neurology applications.
Key Challenges in Medical Image Analysis
Despite technological advancements, medical image analysis presents several challenges:
- Data Variability: Differences in imaging equipment, acquisition protocols, and patient anatomy create variability that affects image interpretation.
- Annotation Complexity: High-quality labeled datasets are essential for training AI models, but manual annotation by medical experts is time-consuming and expensive.
- Noise and Artifacts: Imaging noise, motion blur, and artifacts can obscure diagnostic features and lead to misinterpretation.
- High Dimensionality: 3D or 4D imaging data requires powerful computing resources and sophisticated algorithms to process effectively.
- Clinical Validation: AI algorithms must undergo extensive clinical testing and regulatory approval before real-world deployment to ensure safety and reliability.
The Role of AI and Deep Learning in Image Analysis
AI and deep learning are transforming medical image analysis by automating complex tasks with remarkable speed and accuracy.
Deep Learning Architectures
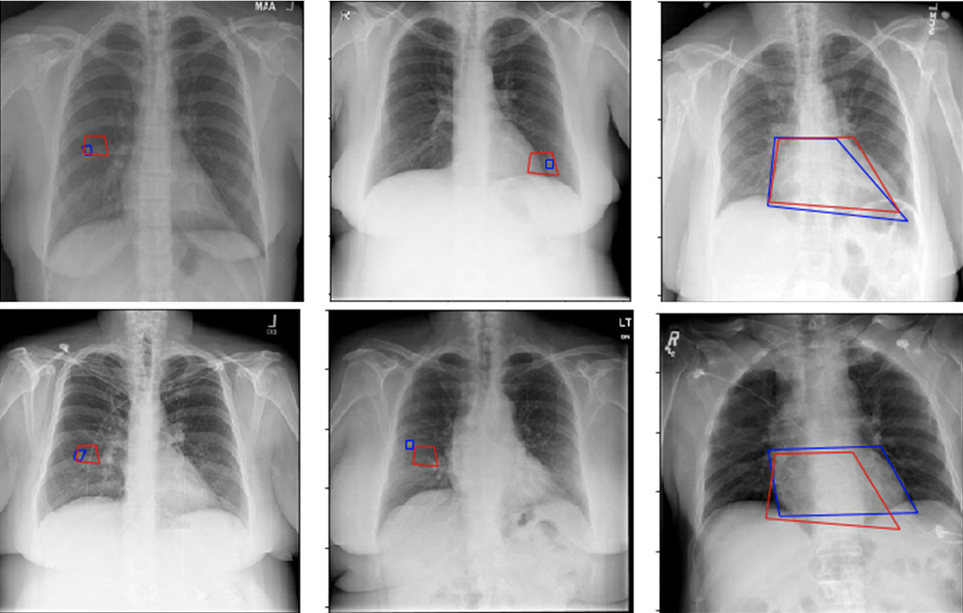
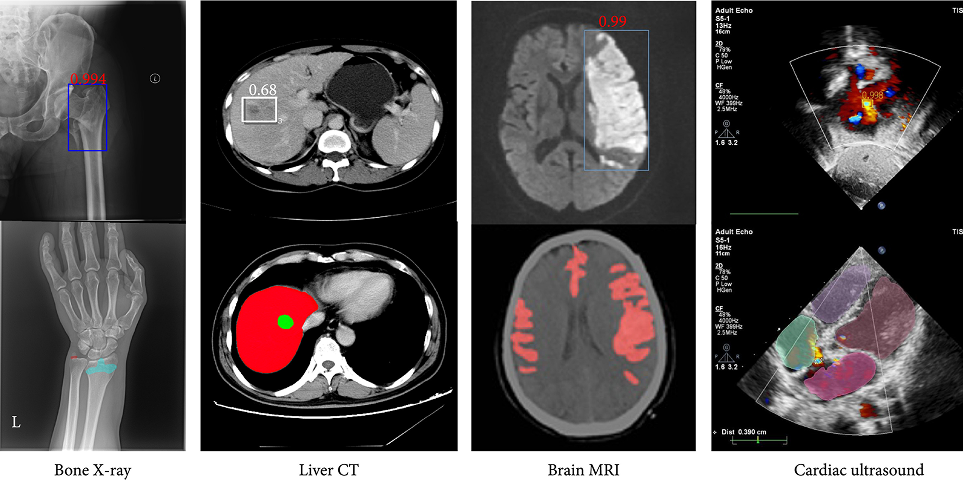
- Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs): Used extensively for classification, detection, and segmentation tasks. For instance, CNNs can differentiate between malignant and benign tumors in radiology.
- U-Net and V-Net Models: Specialized for biomedical image segmentation, these architectures are widely adopted for tasks like organ boundary detection and lesion segmentation in 3D volumes.
Applications of AI in Medical Imaging
- Tumor Detection and Segmentation: AI can identify and delineate tumors in CT or MRI scans, aiding oncologists in treatment planning.
- Organ Localization: Automatic detection of organs helps streamline radiological workflows and ensures consistency in measurements.
- Disease Classification: Models trained on large datasets can classify conditions such as pneumonia, Alzheimer’s, or diabetic retinopathy with high accuracy.
Real-World Applications in Healthcare
The integration of image analysis in clinical practice is transforming several domains:
- Oncology: Detecting cancerous lesions, monitoring tumor growth, and evaluating treatment response using advanced image segmentation techniques.
- Cardiology: Assessing cardiac function through automated echocardiogram analysis and identifying structural heart diseases.
- Neurology: Analyzing brain MRIs to detect early signs of neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s disease.
- Orthopedics: Analyzing bone alignment, joint integrity, and surgical planning for fractures or implants.
The Future of Medical Image Analysis
The future of this field is shaped by several promising trends:
- Federated Learning: Enables AI models to learn from data across multiple institutions while maintaining patient privacy and data security.
- Multi-modal Integration: Combining imaging data with genomics, clinical notes, and lab results for more comprehensive diagnostics.
- 3D and 4D Visualization: Enhancing surgical planning and anatomical modeling through dynamic imaging.
- Explainable AI (XAI): Providing interpretable outputs from AI systems to gain clinicians’ trust and meet regulatory standards.
- Cloud-Based Platforms: Allowing scalable, real-time image analysis and remote collaboration across healthcare systems.
Importance of Data Annotation in Medical Image Analysis
High-quality annotated datasets are the foundation of any successful AI model in medical imaging. Annotation involves labeling organs, tissues, lesions, or anomalies in medical images by trained radiologists or clinicians. These labeled datasets help AI models learn to distinguish between healthy and diseased tissues. Techniques such as semantic segmentation, bounding box labeling, and 3D volume annotations are crucial, especially for complex tasks like brain tumor segmentation or vessel tracking.
However, manual annotation is both resource-intensive and time-consuming. To address this, many healthcare AI companies collaborate with specialized medical annotation teams or use semi-automated tools that speed up the process while maintaining clinical accuracy.
Segmentation and 3D Reconstruction in Diagnostics
One of the most powerful advancements in medical image analysis is image segmentation, where specific regions of interest (e.g., organs, tumors, blood vessels) are separated from the rest of the image. This allows for accurate measurement of volumes, surface areas, and anatomical structures, which is essential in both diagnosis and surgical planning.
Building on this, 3D reconstruction enables clinicians to visualize internal structures in three dimensions, providing a more realistic understanding of patient anatomy. Surgeons use these models to plan complex procedures, such as brain surgeries or reconstructive operations, where precision is critical. These tools are also invaluable in education, allowing students and trainees to explore anatomy in virtual environments.
Regulatory and Ethical Considerations
Deploying AI models in medical imaging requires strict adherence to regulatory standards and ethical guidelines. Models must undergo clinical validation to demonstrate accuracy, safety, and reproducibility across diverse patient populations. Agencies such as the U.S. FDA, CE (EU), and other national bodies require rigorous testing before allowing AI tools to be integrated into clinical workflows.
In addition, ethical considerations like patient data privacy, informed consent, and algorithmic bias must be addressed. Ensuring that AI systems are transparent, explainable, and unbiased is crucial for building trust among clinicians and patients.
Role of Medical Image Analysis in Telemedicine
With the rise of telemedicine, medical image analysis is becoming an integral part of remote diagnostics. AI-driven tools allow healthcare providers to analyze imaging data remotely and share insights in real time. This is particularly beneficial in rural or underserved areas, where access to radiologists and imaging specialists may be limited.
Tele-radiology platforms integrated with AI image analysis can flag urgent cases, prioritize them for review, and even provide preliminary reports—enhancing speed and efficiency in emergency care.
Integration with Electronic Health Records (EHR)
Another major development is the integration of medical image analysis with Electronic Health Records (EHRs). By embedding imaging insights directly into a patient’s health record, clinicians can access a unified view of the patient’s condition, including lab results, prior diagnoses, and visual data.
This holistic approach supports better decision-making, reduces the risk of diagnostic errors, and enhances the continuity of care across departments. AI can even analyze trends over time, alerting healthcare professionals to changes that may warrant further investigation.
Medical image analysis stands at the forefront of healthcare innovation. As imaging technologies advance and AI continues to evolve, this field is set to redefine diagnostic accuracy, speed, and precision. From early disease detection to personalized treatment planning, medical image analysis not only empowers clinicians but also improves patient outcomes and healthcare efficiency. The convergence of data, intelligence, and medical expertise is shaping a future where smarter imaging leads to smarter care.


