Jun 5 2025
medical image analysis
Transforming Medical Images into 3D Models: A Step-by-Step Guide
In the ever-evolving field of healthcare technology, anatomical 3D models are revolutionizing diagnostics, surgical planning, and patient education. By converting traditional medical scans into detailed 3D visualizations, clinicians can now interact with organs and tissues in ways that were once unimaginable.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through how medical image segmentation and 3D medical imaging techniques are used to transform 2D medical scans into lifelike, medical 3D models.
Image Acquisition – Anatomical 3d models
The process begins with collecting high-resolution medical images using tools like:
- CT
- MRI
- Ultrasound
- PET
These imaging techniques provide layered slices of the human body, which serve as the raw data for 3D reconstruction.
Medical Image Segmentation
Medical image segmentation is the backbone of 3D modeling. It involves isolating specific structures (like organs, tumors, or bones) from the rest of the scan.
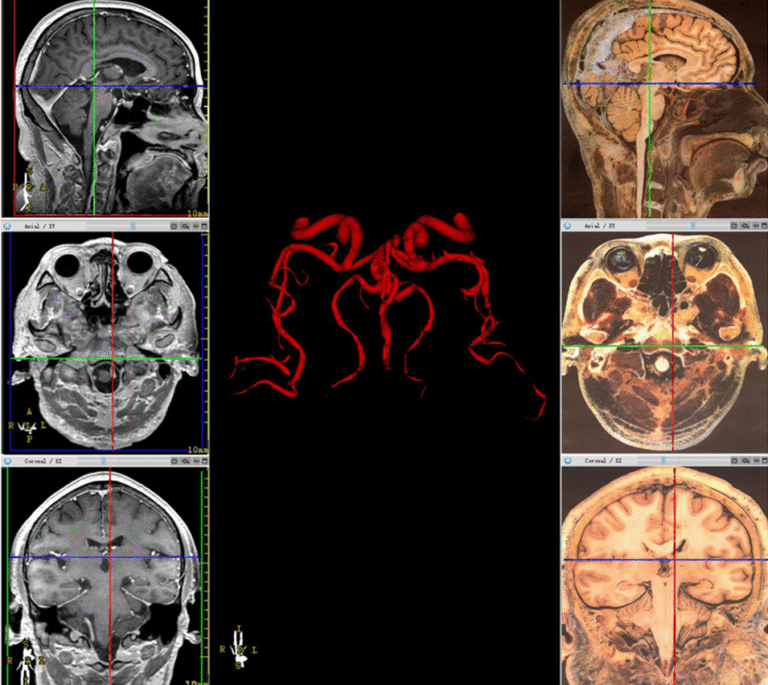
Segmentation done by:
- Manually by clinical annotators, then reviewed by Senior Medical Imaging Specialists & Radiologists.
- Semi-automatically using AI software with expert supervision.
- Fully automatically using advanced deep learning algorithms, followed by expert validation.
This step ensures that only the required anatomy is extracted for 3D modeling.
3D Reconstruction
Once segmentation is complete, the software converts the isolated 2D slices into a 3D model by stacking and rendering them in a volumetric format.
Popular tools for this include:
- 3D Slicer
- Mimics Innovation Suite
- OsiriX
- ITK-SNAP
- Redbrick AI
At this stage, the medical 3D modeling process generates a mesh that outlines the surface of the anatomical structure.
Model Refinement and Editing
Post-reconstruction, the model is refined for accuracy. This may include:
- Smoothing rough surfaces.
- Fixing mesh holes.
- Adjusting the scale and dimensions.
This refined 3D medical imaging data can now be used for educational models, surgical guides, or prosthetic design.
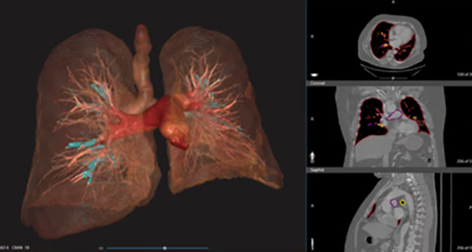
3D Model Print – Anatomical 3d models
The final model can be:
- 3D printed for physical interaction and surgical practice
- Used digitally for simulations, AR/VR-based medical training, or patient consultation
Hospitals and med-tech companies now rely heavily on these anatomical 3D models for personalized medicine and pre-operative planning.
Applications in Healthcare
- Orthopedic Surgery: Personalized implants and bone reconstructions
- Cardiology: Modeling heart structures before valve replacements
- Oncology: Visualizing tumors in 3D for precise removal
- Education: Virtual anatomy training for medical students
The transformation of medical images into 3D models is more than a technical feat — it’s a leap toward patient-specific care and better surgical outcomes. As 3D medical imaging and medical image segmentation technologies continue to advance, expect even more personalized and minimally invasive solutions in healthcare.


