Jan 29 2026
medical image analysis
The Ultimate 2026 Guide to Medical Image Annotation & Segmentation Services
~9 min. read
Medical imaging sits at the core of modern healthcare AI. From radiology and neurology to oncology and cardiology, AI models are increasingly expected to support clinical decisions—not just experiments or proofs of concept. This shift from research to real-world deployment has made large-scale medical image annotation a necessity rather than a choice.
Today’s AI systems demand vast, diverse, and consistently annotated imaging datasets to achieve clinical-grade accuracy. However, medical images are inherently complex: subtle anatomical boundaries, overlapping structures, varying imaging modalities, and case-specific ambiguity make them fundamentally different from natural images. As datasets scale, even small annotation inconsistencies can compound into significant model performance issues.
This is where many healthcare AI teams struggle. Scaling annotation quickly without compromising precision, consistency, and clinical relevance is one of the most underestimated challenges in medical AI development.
This blog breaks down what medical image annotation and segmentation really involve, how they are applied in real-world AI systems, and what healthcare AI companies should look for when choosing annotation services that can scale without sacrificing quality.
What Medical Image Annotation & Segmentation Mean in Healthcare AI
Medical image annotation refers to adding structured information to medical images so that machine learning models can learn from them. These annotations tell an AI system what is present in an image—such as a condition, anatomical structure, or region of interest.
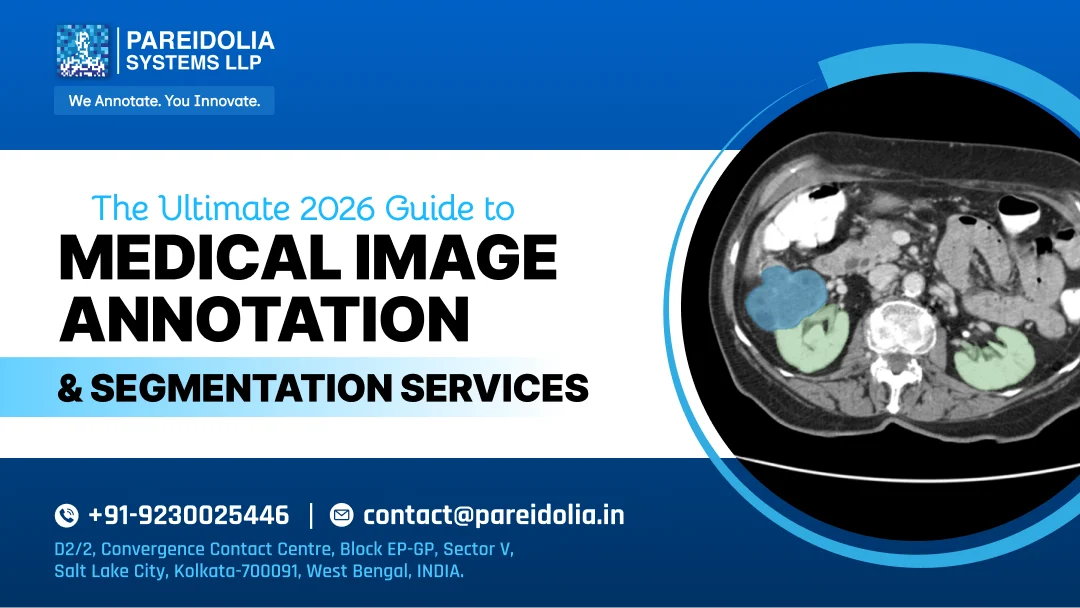
Medical image segmentation, on the other hand, goes a step further. Instead of simply identifying what exists, segmentation defines exactly where it exists—often down to individual pixels in 2D images or voxels in 3D scans like CT and MRI. This level of precision is critical for clinical applications where boundary accuracy directly affects model outcomes.
Why Medical Image Annotation Is Fundamentally Different
In medical AI, annotation quality is not just a matter of model performance—it directly influences reliability, generalizability, and downstream clinical risk. Unlike general computer vision tasks, medical imaging data is inherently ambiguous, modality-dependent, and sensitive to subtle boundary definitions. Inconsistencies and low-quality annotations can significantly limit a model’s ability to generalize across real-world clinical settings, even when advanced architectures are used. This is why medical image annotation demands expert-driven interpretation, rigorous validation, and precision at the pixel or voxel level—especially as datasets scale.(1)
| Aspect | Medical Imaging | Regular Images |
| Ground Truth | Subjective, clinician-driven | Clear, objective edges |
| Precision | Pixel-level for disease boundaries | Broad bounding boxes suffice |
| Expertise Needed | Radiologists essential | Crowdsourced labelers work fine |
| Data Traits | Modality specific artifacts complicate labeling | Clean, plentiful 2D datasets |
| Stakes | Ties to patient outcomes | Mainly benchmark performance |
Because of this, medical image annotation is not a mechanical task. It is a form of data engineering that directly shapes model behavior, reliability, and clinical trust.
Common Annotation & Segmentation Types Used in Medical AI
Common Medical Image Annotation Types
- Image-level labeling: Assigns a single label to an entire image (e.g., presence or absence of a condition). Useful for classification tasks, but limited in clinical interpretability.
- Bounding boxes: Draws rectangular regions around areas of interest. While faster to produce, bounding boxes often lack the precision required for medical applications involving complex anatomy.
- Landmarks: Used to mark specific anatomical points, often in orthopedic, dental, or facial analysis workflows.
Medical Image Segmentation Types
- Semantic segmentation: Classifies every pixel into a predefined category, useful for identifying broader anatomical regions.
- Instance segmentation: Differentiates between multiple instances of the same structure (e.g., multiple lesions).
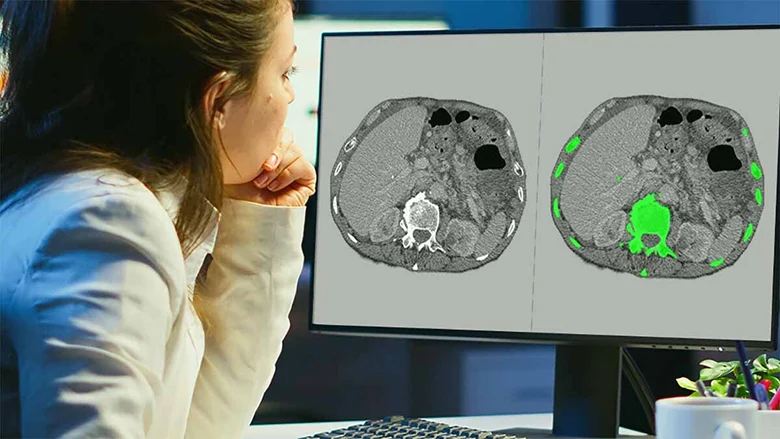
- Pixel-level / Voxel-level segmentation: Provides high-precision boundaries essential for detecting subtle abnormalities and measuring progression.
- 3D volumetric segmentation: Applied to CT and MRI data, enabling spatial understanding across slices rather than isolated images.
Choosing the right annotation or segmentation approach is not merely a technical preference—it is a strategic decision that impacts model accuracy, explainability, and clinical relevance.
Common Annotation Platforms Used in Medical Imaging Workflows
Some of the common annotation platforms used for medical image annotation are:
- RedBrick AI: A collaborative annotation platform commonly used for DICOM-based 2D and 3D medical image segmentation at scale.
- 3D Slicer: An open-source tool widely used in clinical and research settings for advanced 3D visualization and volumetric CT/MRI segmentation.
- ITK-SNAP: A precision-focused tool for manual segmentation, often used in clinician-in-the-loop workflows.
- Custom and in-house annotation tools: Proprietary platforms built to integrate annotation directly into internal data pipelines and model development workflows.
Why Medical Image Annotation Breaks Down at Scale
If annotation quality drops by just a few pixels at scale, how far does that error travel through your model pipeline?
In medical AI, annotation errors rarely stay local. Small boundary inconsistencies propagate through training and validation. (2)
As datasets scale, a few challenges consistently emerge:
- Interpretation drift: Variations in how anatomy or pathology is labeled introduce inconsistency across large datasets.
- Speed over precision: Throughput-focused workflows often compromise pixel- or voxel-level accuracy.
- Oversimplified ambiguity: Edge cases and uncertain findings are forced into rigid labels, weakening model robustness.
- Costly rework: Shortcuts taken early in annotation frequently require correction at scale.
The problem is not scale itself—it is scaling without the right expertise, processes, and flexibility. In medical AI, annotation errors do not stay isolated; they propagate through training, validation, and deployment, directly affecting model reliability and clinical confidence.
Large-scale annotation is now a requirement, but precision must scale with volume, not be sacrificed because of it.
Annotation Platforms & Tools: Why Tool-Agnostic Teams Win
Given the diversity of annotation platforms used in healthcare AI, rigidity becomes a liability.
Many annotation vendors are deeply tied to a single tool or workflow. While this may work initially, it creates friction as projects evolve—whether that means migrating platforms, increasing segmentation complexity, or integrating annotation more tightly with internal pipelines.
For healthcare AI teams, the real advantage lies in working with annotation partners who are tool-agnostic and platform-flexible. Such teams are able to:
- Adapt quickly across tools like RedBrick, 3D Slicer, ITK-SNAP, or custom systems
- Maintain annotation consistency despite platform changes
- Align workflows with existing ML pipelines and data governance requirements
- Support evolving needs, from coarse labeling to pixel- and voxel-level segmentation
In production-grade medical AI, the ability to adapt matters more than the software itself. Annotation teams should fit seamlessly into your ecosystem, not constrain it.
Questions AI/ML Healthcare Companies Should Consider When Evaluating an Annotation Partner
Choosing a medical image annotation partner is not just an operational decision—it has long-term implications for model reliability, compliance, and deployment readiness. Rather than focusing only on cost or turnaround time, healthcare AI teams should step back and examine how annotation is approached in practice.
Here are key questions worth reflecting on:
- How is patient data protected across the entire annotation lifecycle?
From data ingestion to delivery, annotation workflows should be designed around secure access, controlled environments, and clear accountability—especially when working with regulated medical imaging data. - How well does the annotation process integrate with existing tools and pipelines?
As annotation requirements evolve, friction often emerges at the tool or workflow level. Flexible partners are those who adapt to your ecosystem rather than forcing rigid processes. - What level of medical or anatomical understanding informs annotation decisions?
The difference between visually correct labels and clinically meaningful annotations often lies in domain expertise and contextual judgment. - How is consistency maintained as datasets grow and annotation complexity increases?
Scaling annotation volume should not introduce interpretation drift or boundary inconsistencies that compromise model learning. - How are ambiguous cases, edge findings, or borderline structures handled?
Mature annotation workflows acknowledge uncertainty and manage it systematically, rather than simplifying complex cases to meet volume targets. - What safeguards exist to ensure annotation quality remains reliable over time?
Sustainable annotation efforts rely on layered review, feedback loops, and continuous validation—not one-off checks. - How resilient is the delivery model when timelines tighten or priorities shift?
In fast-moving AI programs, the ability to support continuous or round-the-clock workflows can be as important as raw annotation capacity. - How does the engagement scale as requirements change?
Long-term partnerships benefit from predictable cost structures and operational flexibility as datasets, modalities, or segmentation depth evolve.
Why Teams Choose Pareidolia Systems
Medical image annotation is not a one-size-fits-all service. As healthcare AI systems move from research to real-world deployment, teams need annotation partners who can adapt to evolving requirements without compromising precision, security, or delivery timelines.
Pareidolia Systems works with this reality in mind.
- Precision where it matters most
Pareidolia specializes in pixel- and voxel-level medical image segmentation, ensuring that annotations capture clinically meaningful boundaries rather than approximate regions. This level of precision becomes critical as models scale and move closer to deployment. - Domain-informed annotation teams
Annotation is performed by trained experts with medical imaging domain knowledge, allowing ambiguous cases and edge findings to be handled with context rather than guesswork. - Platform-agnostic execution
Whether working on RedBrick, 3D Slicer, ITK-SNAP, Materialise Mimics, or custom in-house tools, Pareidolia’s teams integrate seamlessly into existing workflows instead of forcing process changes. - Adaptable workflows aligned to client needs
Projects evolve—modalities change, segmentation depth increases, and review requirements grow. Pareidolia’s annotation workflows are designed to adapt without disrupting timelines or quality. - Scalable and cost-conscious delivery
Pareidolia supports large-scale annotation programs with transparent, affordable pricing models, helping teams balance precision with long-term sustainability. - 24×7 operational support
With continuous delivery capabilities, Pareidolia enables faster iteration cycles and supports globally distributed AI teams operating across time zones.
Rather than treating annotation as a transactional service, Pareidolia positions itself as a long-term partner—focused on building datasets that are reliable, scalable, and ready for production-grade medical AI.
The Future of Medical Image Annotation: Growth, Challenges, and Priorities
The medical image annotation market is surging. This growth is propelled by AI’s expanding role in diagnostics, treatment planning, and research, where high-quality annotated data drives better healthcare outcomes.(3)
Yet, AI integration faces hurdles like data governance, algorithm robustness, transparency, and regulations. Poor annotations erode clinical trust and model performance in real-world use.
Strategic annotation partners are key, delivering volume alongside pixel-level precision and workflow adaptability. Pareidolia Systems excels here, offering domain expertise across tools like RedBrick, 3D Slicer, ITK-SNAP, and Materialise Mimics, with scalable 24×7 delivery for clinically reliable datasets.